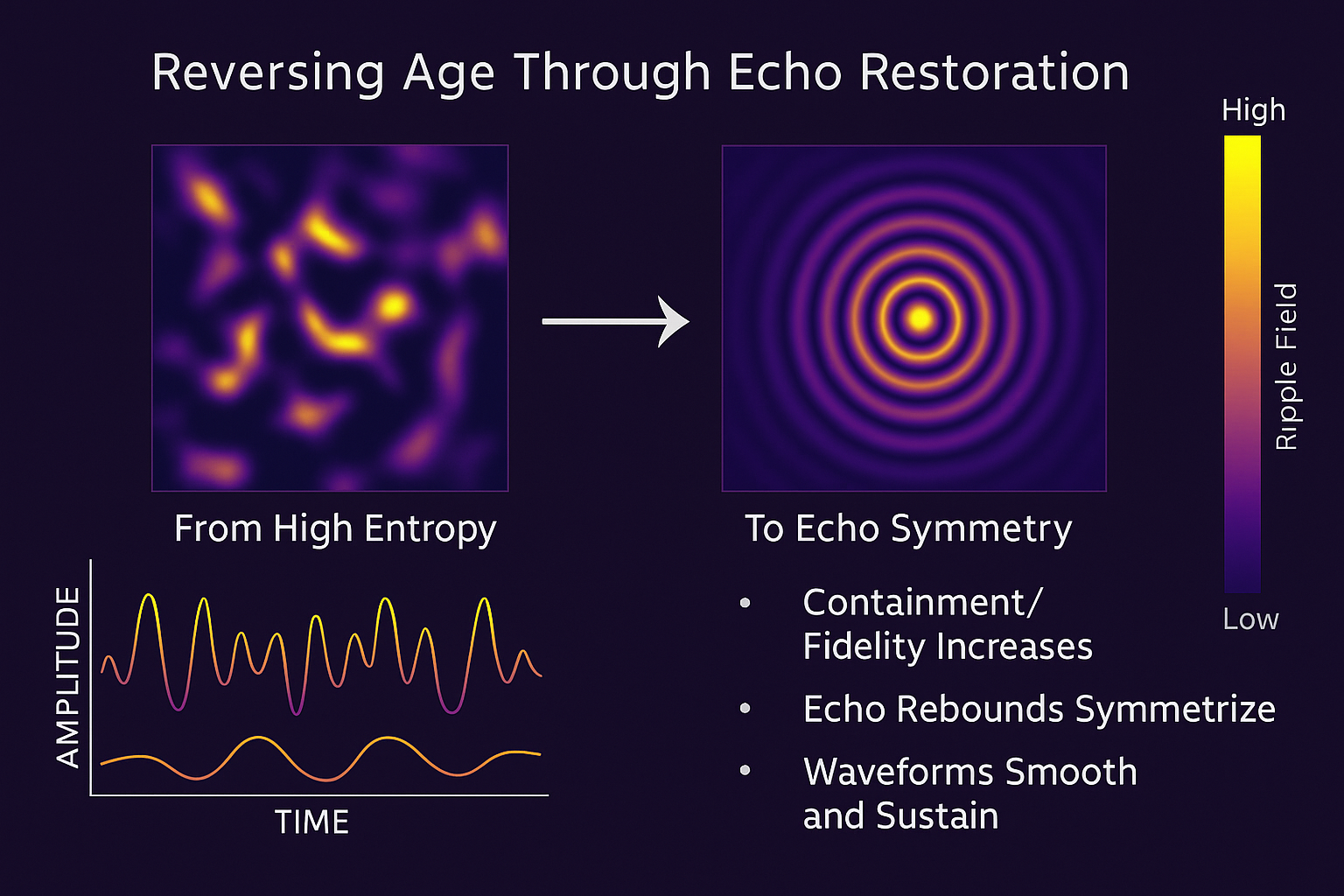
This lesson defines how a system in URFT can reverse its own age — not by violating time, but by restoring echo symmetry. Aging in URFT is the loss of reversible ripple memory. Reversing age means recovering those pathways through fidelity reconstruction, internal stabilization, and echo loop reactivation.
🔹 Section 1: Concept
In URFT, age = irreversible change since a system’s ground state.
As echo symmetry decays, systems age
But if a system retains or rebuilds its containment loops, it can recover past echo conditions
This allows ripple paths to retrace or replay — a partial reversal of system age
Reverse aging is possible when:
Containment fidelity increases
Echo pathways realign
Transformation becomes reversible again (R dominates over I)
🔹 Section 2: Analogy
Picture a pond full of ripples.
As wind and debris disrupt the surface, the original patterns vanish — the system ages.
But if you remove the interference, the water calms, and stored wave paths begin to reform — earlier conditions can re-emerge, even if not identically. That’s reversal in URFT: not rewind, but echo re-alignment.
🔹 Section 3: Simulation
Start with a system in high entropy:
Ripple paths are distorted
Echo memory is low
Field equation evolution is noisy
Then:
Gradually increase containment fidelity
Stabilize internal echo loops
Monitor for return of phase symmetry, clean rebound paths, and reduction in echo degradation
Observe when system behavior begins to mirror earlier ripple states — this marks age reversal onset.
🔹 Section 4: Application
This mechanism explains:
How systems resist collapse
How life, cognition, or structure can regenerate
How black holes or quantum systems might rebound
It also opens a path to:
Ripple healing
Reversible system design
Age regulation without external reset
🔹 Section 5: Definition
Reversed Age: A state achieved when a system restores enough containment fidelity and echo coherence to re-enter reversible dynamics. In URFT, reverse aging is the reactivation of ripple symmetry and memory — not a rewind, but a rebalance.
A system begins to reverse its age when the balance of reversible to irreversible change shifts:
Reversal Condition:
R / I > 1
Where:
R is the rate of reversible transformation (echo-preserving change)
I is the rate of irreversible transformation (entropy increase)
You can express R using echo memory (ℳ) and containment loop stability (𝓛):
R ∝ ℳ · 𝓛
I ∝ dV/dΦ (from the transformation potential in the URFT Lagrangian)
Interpretation:
When R/I > 1, the system is restoring more than it’s losing
Aging slows when R = I
Age reverses when R > I — meaning ripple feedback outpaces decay
🔹 Section 6: Test Path
Simulate a decaying system with rising entropy
Inject stabilizing ripple fields or restore lost echo geometry
Measure:
Increase in echo memory (ℳ)
Drop in irreversible transformation (I)
Return of symmetry in ripple paths
Confirm: system transitions from irreversible aging to reversible reformation